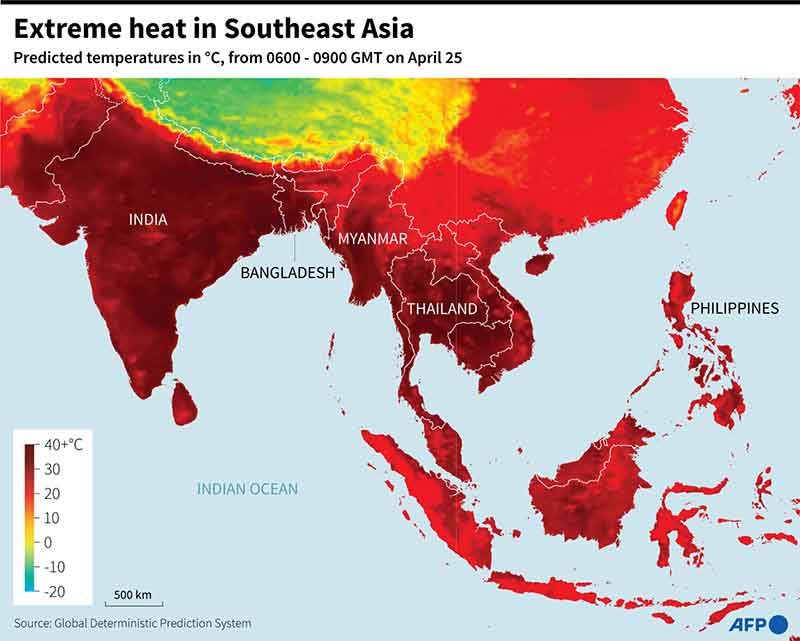
India refrained from signing the Declaration on Climate and Health, a document that was endorsed by 123 nations in the COP28 held in UAE in the first half of December 2023.
The declaration, aimed at addressing the critical intersection between climate change and global health, emphasises the need for swift and substantial reductions in greenhouse gas emissions. It expresses“grave concern about the negative impacts of climate change on health,” and notes the benefits to health from deep, rapid, and sustained reductions in greenhouse gas emissions, including from just transitions, lower air pollution.”
To ensure better health outcomes including through the transformation of health systems to be climate-resilient, low-carbon, sustainable and equitable, the signatories of the declaration commit to promoting “steps to curb emissions and reduce waste in the health sector, such as by assessing the greenhouse gas emissions of health systems, and developing action plans, nationally determined decarbonization targets,” and take health into account while “designing the next round of nationally determined contributions, long term low greenhouse gas emission development strategies, national adaptation plans.”
Why did India not support this progressive declaration? One of the sticking points that India saw at the declaration’s draft stage was its commitment to reduce greenhouse gases for cooling applications in the healthcare sector. India felt that it could not fulfil this commitment in the short run as it would hinder the current high growth rate that the pharmaceutical industry and health services enjoy.
Healthcare is one of India’s largest sectors in terms of revenue and employment. With a public expenditure of 2.2% of India’s GDP, the healthcare industry was estimated at ₹ 30 lakh crores turnover in 2022. In the last 8 years, its turnover grew at 22% per annum, generating 5 lakh additional jobs per year. With per capita incomes on the rise, healthcare expenditure is expected to continue to grow at a rapid pace.
The Indian pharmaceutical industry is the third largest in the world and grew at over 9% per annum in the last decade. India is the largest global provider of generic drugs and accounts for more than 60% of all global vaccine manufacture and 20% of generic drug exports. The industry was valued at ₹ 3.4 lakh crores in 2021 and is expected to treble that value by 2030.
Fossil fuels contribute 75% of India’s total energy requirement and 58% of its power generation. The healthcare and pharmaceutical industries, including their cooling requirement, are completely dependent on India’s carbon-intensive energy basket. Not wanting to disturb the high growth rate expected in these two sectors in the coming decades, India decided to refrain from endorsing the COP28 declaration on climate and health.
Ironically, the Indian delegation to COP28 did not consider the downside of fossil fuel use, particularly in power generation. Fossil fuel-based power plants, 85% of which use the dirtiest of fuels—coal, cause an estimated crop yield loss of ₹ 1.5 lakh crores per annum. Studies estimate that the excess deaths attributable to fossil fuel power generation are about 50 per annum for every GW of installed capacity. With about 250 GW of installed capacity in fossil fuel generation, the number of excess deaths per annum is approximately 12,500 persons. Other impacts that have not been adequately assessed are corrosion of soils and buildings, forest dieback, and acidification of water bodies.
The healthcare and pharma industries are amenable to installing rooftop PV panels as they have large rooftops and the profits to invest in them. If these industries spent just 2% of their combined annual turnover. i.e., ₹ 75,000 crores to replace half the 15 GW of energy they draw from the grid with energy from rooftop PV panels, the environmental injury attributable to them can be reduced significantly.
The continued use of energy from India’s carbon-intensive grid by the healthcare and pharma industries should be called out by the Indian polity as ecocide and genocide, and it must be stopped immediately.
Sagar Dhara Male, Upper caste & class, University-educated, City slicker, Member of the most ferocious predator that ever stalked Earth—humans
Frontier, Vol 56, No. 26, Dec 24 – 30, 2023, https://www.frontierweekly.com/articles/vol-56/56-26/56-26-COP28%20-%20Declaration%20on%20Climate%20and%20Health.html