by Paritosh Singh, Akash Singh & Ashish Kumar Singh
Abstract
Vehicle parking is a major problem in urban areas in both developed and developing countries. Following the rapid increase of car ownership, many cities are suffering from lacking of car parking areas with imbalance between parking supply and demand which can be considered the initial reason for metropolis parking problems. This imbalance is partially due to ineffective land use planning and miscalculations of space requirements during first stages of planning. Shortage of parking space, high parking tariffs, and traffic congestion due to visitors in search for a parking place are only a few examples of everyday parking problems. In major cities, as the development goes on, the parking generation rate increases rapidly which leads to major parking problem. The paper examines parking problem in the city; its different causes and conventional – yet non-successful – approaches. Modern technology has produced a variety of new solutions and techniques in this respect. On-street and off street parking characteristics were analyzed considering the parking statistics which includes parking accumulation, parking occupancy, parking load, average parking duration, parking index/parking efficiency. Some areas, even having sufficient parking capacity suffered from congestion due to improper management and lack of availability of required signs, marking of bays and other smart techniques. The paper reviews new planning trends and creative technological solutions which can help alleviate the strain of the problem. Because car parking solutions are not an end in itself, but rather a means of achieving larger community goals in order to improve urban transportation and make cities more livable and efficient, the paper also discusses the environmental impacts which should be taken into considerations for solutions proposed. Observing the study outcomes, some guidelines have been suggested for optimal utilization of available space. Study outcomes will be helpful for engineers, planners and policy makers
Introduction:
With rapid growth of the metro cities all over the world, the parking generation rate goes on increasing very quickly which creates major problems of parking in most of the urban areas. In the recent years, with the rapid development of economy and exorbitant increase in the motor-vehicles, parking problems in urban areas of metro cities have become increasingly prominent.
In Urban India, however the problem of parking has not been given due importance. Mass transportation systems are generally ignored or do not provide regular, frequent, safe and adequate quality of services. There-by people are relying on the private vehicles, which in turn leads to the extreme traffic congestion and shortage in parking areas. With the preparation of a comprehensive traffic and transportation plan for the city along with the appropriate locating of land uses on the master plan, these problems can be addressed. This system is called “Parking Management”. Parking management can be defined in a broad sense that it is an effective tool for the local government which helps in reduction of single occupant vehicles and encourages the mass transportation facilities to influence the other aspects of parking supply and demand. We have to develop those places which are under authentic parking zones for the better parking supply and provide the possible way of parking for those places too which are under the tag of non parking zones. Cities of hill states are worst-affected, where parking spaces are woefully falling short of the current requirements. During season they are witness long snarls which can be partially attributed to haphazard parking of vehicles on roads.
Literature Review
Number of studies has been done on parking in the past, such as estimation of parking accumulation profiles from the survey data by the cluster analysis technique (Tong, Wong & Leung, 2004) which states that parking supply is an effective means to restrain the car ownership and usage, however acute shortage of parking might drive away commercial and other activities. Also, the search time increases approximately 20 percent in the commuting time (Ommeren, Wentink, Dekkers, 2011). High number of on-street parking spaces along the major road in the urban area affects local traffic operations, especially when traffic is large (Zhenshan, Zhirong, Yi, 2014). They proposed a solution of “Division, Construction, Adjust & Share” for parking management to the Wujiang district’s urban parking problem. Paul C. Box (2004) studied the hazard and congestion due to on-street parking, specially the angular parking, which is useful for the local officials and planners to improve the safety and operation of the traffic. Since, the old areas are pre-planned; there is a limited parking space available which creates spill over. Shuang Li, RuHua Zhang, and Yue-Chun Ge (2017) have carried out the comprehensive survey and analysis of parking facilities in old community in Jinan, China and used the parking supply model based on livable environment to determine the suitable scale of parking supply. A study based on stated preference survey was undertaken by David and Jenny in 2001 to investigate the role of parking pricing and supply as well as the location of parking lot on the demand of the parking in the particular area of the Sydney central business district. Also, haphazard parking due to lack of parking space marks leads to inefficient utilization of the parking lot area. In Greece, the analysis had been carried out (Christina and Constantinos, 2012) regarding the illegal parking behaviour in six different cities for which the data has been collected in the year of 2010. In that, three cities are taken in Athens and other three are smaller Greek cities. It is seen that illegal parking is more in big urban cities due to saturation of parking spaces and also the tendency to park as near as possible to the destination. One of the major solutions to reduce the demand for parking is to reduce or stable the private car ownership and mode shift from private car to public transportation. Parking fee is one of most influencing factors for the mode shift. Recently, Qun Chen et al. (2015) have studied the characteristics of parking in Central Shanghai of Shanghai city, china. The authors have classified the whole survey area based on the land use and analysed parking facilities for the same. Authors also suggested the parking policy for different areas and to use the modern techniques in parking to balance the parking facilities types and to provide choice to parking users.
Research Problem
People prefer to own vehicles because ownership of a vehicle can offer an unmatched combination of speed, autonomy, and privacy. But the fact is that there is no private vehicle is perpetually in motion; most private vehicles spend most of their time at rest, either during working hours or over the night. This means that there should be two places for every car in the city to be parked in. The two places should be at the both ends of every trip. Parking problems in cities and urban areas are becoming increasingly important and have been one of the most discussed topics by both the general public and professionals. The imbalance between parking supply and parking demand has been considered as the main reason for metropolis parking problems. Moreover, the parking system plays a key role in the metropolitan traffic system, and lacking of it shows closed relation with traffic congestion, traffic accident, and environmental pollution. Although efficient parking system can improve urban transportation and city environment besides raising the quality of life for citizens, parking problem is an often-overlooked aspect of urban planning and transportation. Urban planners should seek more efficient and innovative solutions for parking problem on the level of management, planning, and designs.
Research Objectives
The paper examines the problem of car parking in cities and urban areas in order to set general principles and guidelines for parking solutions. To achieve the quality of citizens‟ life the concluded solutions should consider the aspects of planning, management, technology, environment, and aesthetics. The research objectives are: –
- Identifying the causes of parking problem and its negative impacts.
- Examining the different conventional – yet non -successful- approaches provided for tackling the problem on both planning and management levels.
- Studying the innovative solutions which use modern technological means, or which consider environmental and aesthetics aspects in both planning design.
- Learning how parking problem should be solved efficiently and comprehensively according to general principles and guidelines.
Research Methodology
The content analysis methodology is adopted in this research which based on extensive literature concerned with car parking problem in cities and urban areas. In order to achieve the objective of the paper, collected data has been analyzed and categorized according to types of parking solutions on the level of planning, management, and design. The latter includes solutions that consider mechanical and technological innovations and also the environmental aspects. The conclusion and recommendations of the research have been indicated.
The parking demand is directly related to the land use of a particular area. It is common that commercial area having large number of offices will require large space for the parking because the people coming in the offices by private vehicle park their vehicle throughout the day and also the extra space for visitors. The area having market place having fluctuating demand throughout the day depending upon the requirement of the visitors. The demand for parking at weekend will be higher compare to week days.
Common Parking Problems/Issues in Urban India
Parking problem in cities and urban areas means actually that there is a gap between parking demand (number of cars in need for parking spaces) and parking supply (number of parking spaces sufficient to cars in need to park).
This gap is due to several reasons: –
- Most of old and historical cities, especially the capitals, have been planned with narrow streets where there were no cars but carts moved by horses. Also, population densities of these cities at that time were not so high comparing with the current densities of the same cities and of the same areas. As city streets cannot be changed or altered over time, except for some important reasons and in limited cases, these narrow streets become responsible for accommodating all kinds of vehicles in high densities for moving and parking, a load which exceeds their planned capacities.
- In old and existing cities, and as a consequence of invasion and succession phenomenon, changing uses from uses with low rate of cars such as residential to uses with high rate of cars such as commercial or business also contribute to the problem.
- The violation of building codes and zoning regulations – which stipulates, for each area, specific uses of buildings and specific numbers of floors with providing garages in basements. This violation contributes to change all calculations set by planners for providing sufficient parking spaces for cars in these areas.
- Parking on the road, parking above bridges and under bridges, parking on both sides of the road is a common problem that causes inconvenience to the traffic and at the same time in case of any emergency, a person cannot perform his work at the right time. is
- In today’s present time, the number of vehicles in every house is unexpectedly large, due to which the problem of parking is also coming to the fore, the narrowing of the roads, excessive pressure on the road and lack of proper management of traffic is becoming a big problem today.
Urban Planning and Development initiatives:
Following are list of urban planning and development initiatives and similar plans taken up by PWD for improvement of the urban mobility and parking system within city.
In relation to the parking strategy, as laid down in the Master Plan for Holistic Development of urban area or City, the target was to reduce the number of the parked cars on street, and hence the public space can be used by pedestrians. The next goal related to parking in the Holistic Development Plan is to maintain or slightly increase the total number of parking spaces.
City Development Plan –
This is what the Sikkim transport department has told residents of the state where, as almost everywhere in India, cars parked along roads choke traffic.The department issued a notification this month making it mandatory for buyers to produce an availability-of-parking-space certificate before they can get their vehicles registered.Consumer rights and automobile industry sources described the rule as a first in the country and said it might not stand the test of a legal challenge.The City Development Plan should prepare under the government of Indian scheme of smart city development. There should be major proposals related to the Decongestion Model for the city important place The decongestion model for City should predominantly addresses three main issues, apart from the change in traffic directions:
- Bus Rapid Transit,
- Parking strategies, and
- Pedestrian Environment.
Parking Strategies– Developer should identify various parking zone to ensure proper working of the decongestion model. It recommends formulation of appropriate parking policies, including parking hours and rates, for all residential areas around the city to discourage haphazard parking around the proposed parking sites. The identified parking locations are mainly divided into three different categories:
- Off-site multi storesparking – Multistory parking facilities in the peripheral areas for the person, who is commuting from the peripheral areas to city hotspot area/ main market area. Parking site location and parking capacity should be display at interchange transit point from where the hop on hop off buses can be easily accessible.
- On-site parking – Validate government structures like P.W.D. garage and other government buildings with the possibility of providing enough parking spots, like conventional center and Municipal Market, have also been considered as on-site parking areas. Multi-level parking would be the best option to tap the fullest parking potential of these spots.
- On street parking – All designated parking streets in the potential area will have on street parking along them; typical road widths have been proposed for four-wheeler and two-wheeler parking.
Some of the key recommendations of this Plan with respect to parking management are as follows –
- Facilitate organized parking for various types of vehicles
- Adopt smart parking technologies by delineation and numbering of parking space along with parking sensors, providing parking information via internet and phone, and provision of parkingmeters.
- Allocate parking bays for auto rickshaws at crucial nodes such as bus terminals, busycommercial areas, shopping malls, theatres etc., with proper signages and way findings.
- Make all on-street and off-street parking as pay and park
- Keep a provision for reducing parking charges during off-peak hours and discounted parking rates for the off-street parking
- Encourage short term parking by adopting telescoping parking charges which increase with the duration of parking
- Make a provision for displaying parking charges for an off-street parking facility
- Make a provision to allow free usage of the off-street parking spaces against bulk payments during special events
Types of Parking Systems adopted in Indian cities

Smart Parking Solution:
It is imperative to use Smart Parking Technology to address various challenges related to unorganized parking management. The complete end to end smart parking solution comprises a combination of various components and levels such as vehicle detection sensors, cameras with automated vehicle license plate recognition technology, smart meters, smart payment for parking, and parking assistance by digital signage and navigation apps. It can often involve low-cost sensors and smartphone-enabled app-based navigation system and payment systems that allow drivers to identify the available spaces and reserve their spot in advance. Parking system can be broadly categorised as on-street and off-street. The off-street parking can be a gated plot-based system or a multilevel car parking system.
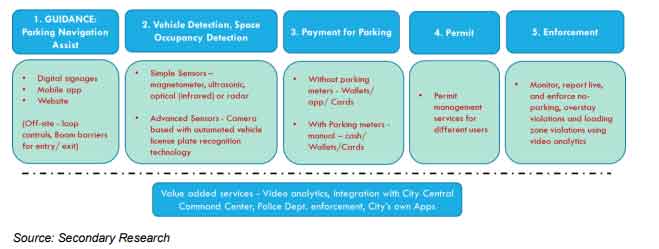
Smart parking solution example:
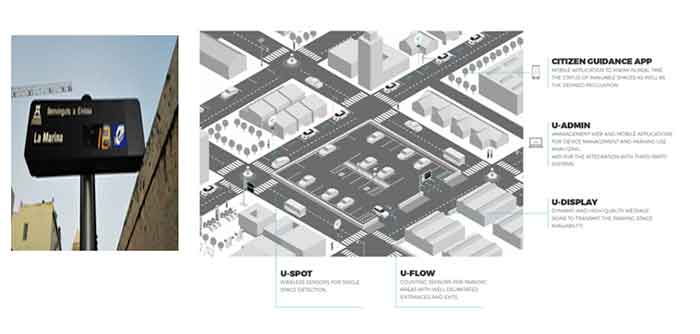
Barcelona, Spain – Smart Parking System –
The solution for Park and Ride was installed in 10 areas of Barcelona. The data captured by the installed sensors is transformed into useful information which transmits the availability of free spaces to the users through the app. This way, drivers are informed about the availability of spaces in these parking areas so that they can go directly to the areas with free spaces. The solution is a win-win since it satisfies both the needs of citizens and those of public administrations.
Details of the installed system:
- U-Flow14 counting sensors to inform about the availability of free spaces.
- U-Spot15 single space sensors to inform about the availability of reserved spaces (electric vehicles, taxis, etc.)
- Integration with multimodal platforms and user information app for the citizens to know the status of available parking spaces in real time.
- Management web and mobile applications for device management and parking use analyzing.
How it works:- - The driver goes to a parking area and accesses it through a well-defined entrance. The U-Flow sensor installed at this entrance detects that the vehicle drives over it and sends the information to the platform.
- The platform collects the data and recalculates the availability based on the total capacity of the parking vs this new access and sends the updated data to the dynamic message signs and/or the user apps, indicating one less free space in this case.
- When the vehicle exits the area and passes over the U-Flow sensor installed in the exit lane, the process takes place in reverse. The system transmits the updated data indicating one more free space to the total available in the parking area.
- When reserved parking spaces are monitored with U-Spot sensors, they detect vehicles parking over and send the information to the platform. It can be deduced from normal space availability and information is given to the users according to the defined space category.
- At the U-Admin platform, the manager can handle the published information, as well as configure, supervise, and consult all the system’s activity.
Key feature and Components for Smart parking solution : –
Vehicle detection –The sensor shall be intelligent and accurately detect if the car space is vacant or occupied. Appropriate sensors shall be chosen based on the type of the parking spot and its external conditions. The sensor shall be able to detect a vehicle irrespective of the depth or height of sensor installation. Each sensor shall have an accurate and real time feedback mechanism to be detected automatically by the system in case of faults.
Informative digital display panels –The display panels units shall indicate available spaces for each parking aisle, total parking spaces and parking availability and shall be able to be customized by software. The display panel shall be easy to understand. The contents to be displayed shall be in local language, Hindi and English.
All city entry point, round about or crossing with traffic system should have a big display unit of parking space available throughout city so that commuter can easily point out the parking space availability and do the advance booking of space.
Mobile Application and Web Portal for Smart Parking-A Citizen App/particular city app and Web Portal are required as a part of Smart Parking Solution. This app should detect the current GPS location of the user and askedon the final destination entered by the user, the nearest available parking spaces are shown using maps in decreasing order of distance and if user decides to reserve it, reservation is done with payment done from e-wallet/Credit or Debit Cards or after physically going there in which case the parking lot might or might not be available.
Number of vacant parking slots in a parking on map should also be shown to user, Users shall be able to locate alternate routes and parking lots after seeing the traffic congestion feed. Limit set on theadvance time to reserve (six hours) except premium and periodic paid parking .Cancellation for the spot shall be provided in case of reservation. For this appropriate concession time for cancellation without penalty fee shall be configurable and also queuing facility as soon as spot fails vacant.
Space purchasing and permitting – Commuter can easily buy or book space online by using mobile application or web portal, they must be provided by a token for space booking confirmation to avoid any grievances while parking.
Payment portal –The payment facility shall be available through app, website and through handheld PoS with various payment options – e-wallet, Credit & Debit Cards, and cash.
Grievance redressal system– The grievance redress system should be an integral part of the website and mobile app where people can lodge a complaint about issues related to the parking system and their queries need to be resolved in a timely manner.
Integration of parking zone with city smart parking solution application:
Local appellate authorities should come with a plan to online integration and combining all parking zone or space of representative city. These must include all government parking space, private parking space of shopping mall, residential societies, hospitals, religious place etc.
Earning potential for individual- Authorities should also allow for individual can sell his parking space city portal of smart parking when one is not using. All residential colony , societies or residential tower can also registered itself on smart parking portal and sell parking space while it is vacant as most of resident are commuting for office or any purposes then the space is unused so they can sell this space for temporary parking on a hour basis.
This will be an additional earning for individual, residential societies, religious place or anyone who has space for parking.
Benefits from the Smart Parking Solution:
The benefits for the city include improved traffic flow, less congestion, and better mobility and living conditions. It further helps in getting additional revenue through increased capture rates and pricing changes powered by analytics.
Smart parking can significantly curb air and noise pollution levels through sustainable urban mobility, saving time and energy, reducing traffic problems, and bringing air and noise pollution down.
A good smart parking system has several social benefits as well. Some of the direct and indirect social benefits are – increase in personal safety at night, reduction in accidents and car damage, minimizes theft, increases safety for pedestrians, provides accessible parking for all users including disabled and parents with children, creates transparency in pricing among citizens and parking managers thus avoiding conflicts, reduces anxiety among the drivers thus reducing the stress levels and unnecessary vehicle speeding and honking etc.
Local Business Benefits with ease of parking, resulting in greater customer footfall. The ability to generate targeted offers and promotions for citizens, based on parking data.
Citizen benefits by reduced circling, leading to savings in time and fuel, less congestion and general improvement in quality of life.
However, that is only a part of the solution, and that, too, the easier part. The harder part, as well as the longer-term solution, is to improve and extend public transport. The West, along with several developed Asian countries like Japan, Singapore, South Korea, and Taiwan have gone about it the right way. They have made it very costly for the motoring public to drive and park in their main cities during working days. So, only the affluent can afford it. However, at the same time, they have made their public transport so good that the vast majority of the people happily use it, even the relatively well off. Many of them can afford to buy a car, but they do not as they are happy using public transport. But if they do decide to own a car, they usually keep it at home and use it only on weekends to go to the countryside or into town as it is much easier, and cheaper, to park than on working days.
References :
- Arnott, R. & Rowse, J., 2009. Downtown parking in auto city. Regional Science and Urban Economics, 39(1), 1-14.
- Azari, K. A., Arintono, S., Hamid, H. & Rahmat, R. O. K., 2013. Modelling demand under parking and cordon pricing policy. Transport Policy, 25, 1-9.
- Box, P. C., 2004. Curb-parking problems: Overview. Journal of Transportation Engineering, 130(1), 1-5. Census 2011, Government of India, 2011.
- Chen, Q., Wang, Y. & Pan, S., 2015. Characteristics of Parking in Central Shanghai, China. Journal of Urban Planning and Development, 142(3).
- , H. L., Chin, S. M., Franzese, O. & Hwang, H., 2005. Estimating the Impact of Pickup- and Delivery-Related Illegal Parking Activities on Traffic. Transportation Research Record: Journal of the Transportation Research Board, 1906, 49-55.
- Hensher, D. A. & King, J., 2001. Parking demand and responsiveness to supply, pricing and location in the Sydney central business district. Transportation Research Part A, 35, 177-196.
- IRC:SP:12 “Guidelines for Parking Facilities in Urban Areas”, Indian Road Congress, 2015.
- Li, S., Zhang, R.-H. & Ge, Y.-C., 2017. Research on the Parking Supply Strategy of the Old Community Based on Livable Environment, 17th COTA International Conference of Transportation Professionals, 4093-4099.
- Litman, T., 2009. Transportation elasticities: How prices and other factors affect travel behavior. Victoria Transport Policy Institute
- Ommeren, v. J., Wentik, D. & Dekkers, J., 2011. The real price of parking policy. Journal of Urban Economics, 70(1), 25-31.
- Spiliopoulou, C. & Antoniou, C., 2012. Analysis of illegal parking behavior in Greece.. Procedia – Social and Behavioral Sciences, 48, 1622-1631.
- Tong, C. O., Wong, S. C. & Leung, B. S. Y., 2004. Estimation of parking accumulation profiles from survey data. Transportation, 31(2), 183-202.
(Dr. Paritosh Singh is an Assistant Professor of Sociology from DBS PG College, Dehradun, He has more than 20 years research experience in the field of Gerontology, Rural Sociology, Industrial Sociology, Gender Issues, Social Psychology and related subject.
Akash Singh, PGDM (marketing), MPM ( Pune University),working as a international business development professional in polymer &plastics industry. He has also worked in different global construction companies.
Ashish Kumar Singh is a doctoral candidate of Politics at the National Research University Higher School of Economics, Moscow, Russia.)