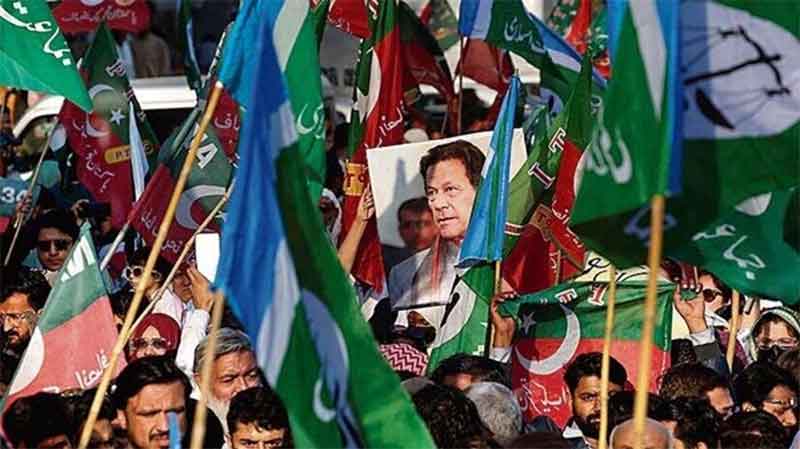
Scheduled for February 8, the upcoming elections for Pakistan’s National Assembly and provincial assemblies hold significant importance against the backdrop of numerous upheavals in the country. Notably, the recent arrest and conviction of the former Prime Minister, Imran Khan, adds a layer of complexity. On January 31, Khan received a 14-year prison sentence, adding to his existing three-year jail term for corruption. In addition, last month, he was handed a 10-year prison sentence in a separate case filed against him, accusing him of leaking classified state documents.
The nation finds itself entangled in a complex web of economic difficulties, with inflation, unemployment, and a pressing capital crisis casting a shadow over its prospects. The specter of poverty looms large, exacerbating social inequalities and hindering the overall well-being of the population.
How Are Representatives Elected in Pakistan?
Under a parliamentary system of government, Pakistan operates with a two-chambered parliament, consisting of the National Assembly and the Senate. The upcoming elections will decide the composition of the National Assembly and the four provincial assemblies—Punjab, Sindh, Khyber Pakhtunkhwa, and Balochistan.
The National Assembly, comprising 336 seats, has 266 directly elected through single-member constituencies using the first-past-the-post system. Additionally, there are 60 seats reserved for women and 10 for minorities. The distribution of women’s reserved seats among parties is proportional to their provincial seat tally, while minority seats are allocated based on each party’s overall seat count.
Following this, members of the provincial assemblies elect 100 members of the Senate, which serves as the upper house of the Pakistani parliament.
The party or alliance securing the majority of seats in the National Assembly gains the privilege of electing its leader, who subsequently assumes the position of prime minister.
Key Parties
The political landscape in Pakistan is marked by several prominent parties, each led by influential figures. The Pakistan Muslim League (Nawaz) (PML-N) is under the leadership of former Prime Minister Nawaz Sharif, while the Pakistan People’s Party (PPP) is headed by former Foreign Minister Bilawal Bhutto Zardari. Imran Khan leads the Pakistan Tehreek-e-Insaf (PTI), and Maulana Fazlul Haq leads the Jamiat Ulema-e-Islam Pakistan (Fazl).
The Election Commission of Pakistan (ECP) has refused to grant the Pakistan Tehreek-e-Insaf (PTI) its designated electoral symbol, the cricket bat. Consequently, a majority of its candidates are now compelled to participate in the election as independents. Imran Khan, the leader of PTI, has been disqualified from participating in the ongoing elections. He is barred from holding any public office for the next decade.
Military Has Its Role and History
Once a figure endorsed by the Pakistan army, Imran Khan has transformed into their primary adversary. The discord originated with the military’s appointment of Lieutenant General Nadeem Ahmed Anjum as the ISI chief against Khan’s wishes along with Khan’s visit to Russia. The latter showed Pakistan’s aggressive neutral position at the beginning of the Ukraine-Russia war, which could have upset the US. Later, Khan’s supporters vandalized one of the generals’ residences after his arrest. The generals aimed to remove him, and now they have accomplished their objective.
However, Pakistan’s political class and its military have historically experienced a complex relationship of collaboration and conflict. Throughout Pakistan’s history, military interventions have been a recurring theme. A pivotal instance occurred in 1958 when President Iskander Mirza declared martial law, nullified the constitution, and shuttered the national and provincial assemblies. General Mohammad Ayub Khan assumed control, marking the onset of military rule. Since then, Pakistan has experienced multiple military interventions.
According to the Pakistan Army Act, the armed forces’ duties include protecting the nation from outside threats and aggression as well as supporting civil authority when necessary. On policy topics, however, differences between the civilian and military governments have frequently occurred. The military has taken power on several occasions by using opposition parties as tools.
Pakistan consistently spends a significant portion of its budget to defense, with the 2022 allocation reaching 17.9 percent of GDP. This is a significant figure, particularly for a country where the per capita income in 2022 stood at $1588.9, equivalent to approximately $4.35 per day.
Key Concerns: Issues Shaping the Election Landscape
In Pakistan, the current economic landscape is characterized by a stark reality as inflation has surged to unprecedented levels, exceeding 30 percent and reaching a 50-year high in the year 2023. In January 2024, it stood at 28.3 percent. This economic turbulence is further underscored by the country’s position in the region, where its GDP, per capita income, and GDP growth are among the lowest. Persistent challenges in terms of high unemployment and inflation rates contribute to the overall economic strain.
According to the UNDP’s Human Development Index, Pakistan is positioned at 161st out of 191 countries, indicating low achievements in crucial areas such as health, knowledge, and living standards. This places Pakistan among the 31 countries globally with the lowest human development levels. The poverty rate in Pakistan was at 39.4 percent in the year 2022.
The situation was further aggravated by the devastating floods experienced in the country in 2022. The floods not only caused widespread damage to agricultural land and critical infrastructure but also had a cascading effect on the overall economy. The aftermath of the floods triggered a surge in inflation, particularly impacting food prices, and increasing the economic hardships faced by the people.
The Interconnected Challenges of Neoliberal Capitalism in Pakistan
The escalating cost of living, rising unemployment, and the specter of stagflation—all intertwined with the limitations of growth—are symptoms of a larger crisis rooted in neoliberal capitalism. This predicament is not exclusive to a particular regime; rather, it stems from the overarching influence of a neoliberal framework that hinders effective crisis management by successive governments. The structural issues at play persist regardless of shifts between political parties or military dictatorships.
The challenges at hand are embedded in Pakistan’s position within the global political economy of neoliberal capitalism. Pakistan finds itself struggling to compete, leading to a significant socio-economic toll.
Pakistan is increasingly becoming the working-class backyard of international capital, with its ability to produce a workforce destined to work abroad, making products that the domestic working class can barely afford. With an annual exodus of over 800,000 individuals seeking employment abroad, a new underclass is emerging within the nation, comprised of individuals keen on obtaining employment that the country is not able to offer.
A significant aspect contributing to Pakistan’s economic challenges is its heavy reliance on foreign loans, often acquired at high interest rates. The country currently operates on these loans, facing the formidable task of repaying a substantial debt amounting to $80 billion within the next three years.
The ongoing crisis in Pakistan cannot be resolved simply by swapping one political party for another. It is intricately tied to deep-seated issues of inequality, concentrated power in the hands of a few, and a lack of commitment from leaders to present a viable alternative. The ability of a new political entity to overcome these challenges remains uncertain. Nevertheless, these elections carry significant weight as the population is enduring hardship, skepticism towards the electoral process is widespread, and the nation appears to be spiraling into an uncertain future with no clear path of recovery.
Pranjal Pandey, a journalist and editor located in Delhi, has edited seven books covering a range of issues available at LeftWord. You can explore his journalistic contributions on NewsClick.in.
This article was produced by Globetrotter.