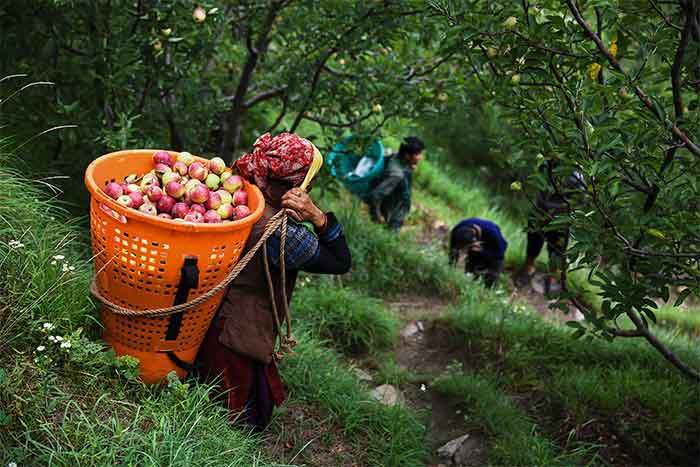
Cultivating temperate fruits, especially apples, plays a crucial role in shaping the economic landscape of India’s hill states like Himachal Pradesh and the hilly areas of Jammu and Kashmir. These regions have difficult terrain that limits heavy industries, making it strategic to grow high-value crops like apples to sustain the economy. The backbone of this sector is the interplay of robust market and input linkages, which significantly contribute to the livelihoods of the local population.
Economic Importance and Agricultural Dependency
The geographical constraints of these hill states limit the feasibility of heavy industries, prompting a strategic shift towards agriculture. Apple cultivation, known for its high-quality produce, has become a linchpin for these regions. The states have actively sought to strengthen both forward and backward linkages in the apple cultivation ecosystem, fostering a sustainable and interconnected agricultural sector. This approach not only provides economic stability but also enhances the overall prosperity of these picturesque areas.
Despite the evident economic significance, the apple sector in Himachal Pradesh faces a formidable challenge – the unpredictable and increasingly erratic climate conditions. Traditionally, the state experiences consistent snowfall from December to late February, essential for the optimal growth of apple trees. Western disturbances play a crucial role in bringing snowfall and rainfall to northern India during this period, creating the conducive environment required for apple cultivation.
Climate Challenges and Changing Patterns
The impact on the apple crop is particularly significant in the hilly districts, where approximately 6 inches of snowfall occurs at regular intervals. This provides the necessary moisture and contributes vital chilling hours essential for optimal growth. The flowering stage in April requires ample sunshine, and rainfall in July, just before plucking, is crucial for successful apple cultivation. However, recent years have witnessed substantial changes in these climatic conditions, posing a significant threat to the apple orchards.
A case in point is the year 2022, when Shimla experienced an unusual dry spell, receiving less than 4 inches of snowfall for a brief period. Unlike the regular snowfall observed in the past, this irregularity had cascading effects on the subsequent monsoon and summer months of 2023. The repercussions of these unusual weather patterns were widely discussed, especially the havoc wreaked by heavy rainfall in Himachal Pradesh in 2023. Unfortunately, the impact on agriculture, specifically the apple orchards, received inadequate attention.
Impacts on Apple Orchards and Agricultural Practices
The erratic and heavy rainfall, coupled with hailstorms in early April 2023, proved devastating for apple orchards. Flowers and buds on the trees were destroyed, significantly reducing the expected apple yield. Recognizing the vulnerability of the sector, the government initiated the distribution of anti-hail nets to farmers. However, implementing this solution has proven more feasible for larger farmers, given the associated costs and delays in securing subsidies. Consequently, small-scale farmers rely on prayers to safeguard their orchards.
Aside from the direct impacts on orchards, the essential road networks, serving as the main modes of communication for farmers to transport their produce to markets, were severely affected. This not only delayed the delivery of produce but, in several villages, farmers were entirely unable to reach markets. In the Nankhari block, a significant apple-producing area in Shimla district, the main road connecting Narkanda pass to Nankhari remains unmaintained, adding further distress to already burdened farmers.
Underreported Agricultural Crisis: Post-Harvest Losses and Market Challenges
What transpired in the 2023 rainfall received insufficient coverage, particularly the profound impact on the apple industry. Aarthiyas (commission agents) and traders encountered challenges purchasing in Mandis (wholesale markets) due to the destruction of various roads. Even when farmers managed to bring their produce to the main markets, auctions were delayed for several days. The apples, adversely affected by untimely rainfall and hailstorms, not only suffered in quality but also experienced significant post-harvest losses, although not officially quantified.
This underreported agricultural crisis sets the tone for subsequent challenges. The heavy rainfall led to topsoil erosion in many apple belts of the state. Consequently, the inputs required for production are anticipated to increase significantly. This unwelcome news arrives when the cost of inputs for apple cultivation has already surged, especially in the aftermath of the COVID-19 pandemic. Adding to the complexities, various fertilizers and pesticides, once readily available in government depots, are now scarce, putting immense pressure on farmers to maintain, if not increase, their production levels.
Future Challenges and Economic Pressures on Farmers
As the apple sector grapples with the aftermath of unprecedented weather events, the repercussions set the stage for considerable challenges in the upcoming seasons. The heavy rainfall, causing topsoil erosion, not only necessitates increased inputs for production but also presents economic hurdles for farmers. The rising costs of inputs, exacerbated by the scarcity of fertilizers and pesticides, create a daunting scenario for those engaged in apple cultivation.
Farmers now face the formidable challenge of sustaining their production levels and matching or surpassing previous years. This pressure comes when the agricultural community is already grappling with economic uncertainties and disruptions caused by external factors.
In conclusion, the economic importance of cultivating temperate fruits, particularly apples, in the hill states of India cannot be overstated. However, the sector faces multifaceted challenges, primarily driven by the changing climate patterns and their adverse effects on traditional agricultural practices. The 2023 rainfall, often overlooked in the broader narrative, underscored the vulnerability of the apple industry and the need for comprehensive strategies to bolster resilience and sustainability in the face of evolving climatic conditions. As farmers navigate these challenges, policymakers, agricultural experts, and the wider community must collaborate to devise solutions that safeguard the economic backbone of these picturesque regions.
Anchal Kashyap is a third year PhD student at Jindal School of Government and Public Policy